Relative Pressure and Absolute Pressure
What is it? And when to use a Relative Pressure level probe and when an Absolute Pressure probe to measure the water level?
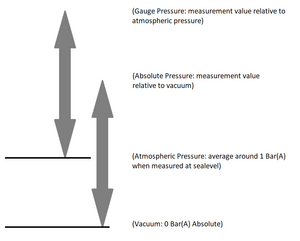
Pressure: what is what?
Vacuum : the absolute zero point = 0 Bar
Absolute pressure : measurement where the reference is vacuum
Atmospheric pressure : measured relative to Vacuum
Barometric pressure : same as Atmospheric pressure
Relative pressure : measurement relative to a fixed point (relative to atmospheric pressure)
Gauge pressure : same as Relative pressure
If we assume that (in this example) the Atmospheric pressure is 1 Bar(A), a measurement with a Gauge pressure measuring instrument will be 1 Bar higher than when we do the same measurement with an Absolute pressure measuring device.
When measuring water level with a pressure probe there are 2 possibilities: using a Relative Pressure probe or using an Absolute Pressure probe.
One thing is obvious: atmospheric pressure changes constantly, so using a Relative Pressure probe (that refers to atmospheric pressure) makes it necessary to have this reference pressure available in the sensor. For this purpose a specially reinforced measuring cable with Goretex membrane pressure-compensation line is used.
This pressure compensation line is being protected against condensation by a silica gel cartridge.
When using an Absolute Pressure probe it is necessary to compensate the measurement value of the Absolute Pressure level sensor for atmospheric changes. In this case a separate sensor like the Baro-Dipper can be used as reference to the atmospheric pressure. In a network of Absolute Pressure level probes it is often sufficient to use only 1 compensation probe.
When you need advice on the best solution for your specific pressure level measurement application we are happy to assist. Call or mail us!